

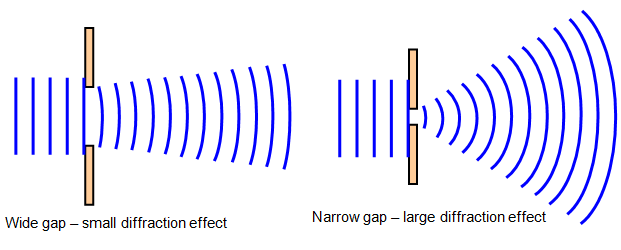
We can continue this reasoning along the entire height of the slit to conclude that the condition for destructive interference for the entire slit is the same as the condition for destructive interference between two narrow slits a distance apart that is half the width of the slit. An alternative picture for photon diffraction had been proposed describing diffraction by a distribution of photon paths determined through a Fourier. Similarly, the source just below the top of the slit will interfere destructively with the source located just below the middle of the slit at the same angle. Diffraction, in general, is the bending of waves around a small. The student is expected to: (A) examine and describe a variety of waves propagated in various types of media and describe wave characteristics such as velocity. Each point on the wavefront emits a wave at speed, v. where s is the distance, v is the propagation speed, and t is time. The transverse nature of light can be demonstrated through polarization. Like all electromagnetic waves, light can travel through a vacuum. The wave nature of light was first illustrated through experiments on diffraction and interference. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a secondary source of the propagating wave. Infinitely many points (three shown) along length d. Diffraction is the interference or bending of waves around the corners of an obstacle or through an aperture into the region of geometrical shadow of the. The system of waves includes sound waves, light waves, electromagnetic waves, water waves, etc. Diffraction is a process in which a beam of light travels through a gap or around a barrier, and spreads out as a result. The principle can be shown with the equation below: (26.2.1) s v t. Light is a transverse, electromagnetic wave that can be seen by the typical human. Diffraction is the interference or bending of waves around the corners of an obstacle or through an aperture into the region of geometrical shadow of the obstacle/aperture.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
